Salary vs. Hourly Pay, which is better?
Future of Work / 22 Jun 2022

When hiring an employee, an organisation needs to think about different aspects. One of the most important ones of all is whether to offer the person a salary or a pay per hour position, like a GoGetter!
Usually, salaried employees do not get paid on an hourly basis. Instead, they receive a monthly amount as outlined in their employment offer letter.
Conversely, an hourly worker receives a specified amount per hour for their work. He/she may receive the pay for total weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly hours.
Determining Salary or Hourly Pay.
From an organisation’s perspective, determining salary vs. hourly pay while hiring employees is crucial. Similarly, employees are most likely to think, “Is it better to be paid a monthly salary or hourly?”
Whether paying salary or hourly wage is better depends on an organisation’s requirements, budget, and also the potential employees’ skill sets, experience, needs, and preferences.
In the next sections, we will find the answer to the question ”What’s the difference between hourly and salary pay?”
What is Hourly Pay?
An hourly rate is a specific amount that a worker receives for an hour of work. For example, if the rate per hour is RM10, and the person works 8 hours a day, he/she would earn RM80 that day. This is usually classified as a temporary position rather than a permanent employment.
For hourly wages too, a worker has to pay the same taxes and other deductible contributions from the final amount. The worker will get the remaining amount either through cash or bank deposits. However this might make it difficult for hourly paid workers to obtain bank loans for example.

Example caption: Example of how much businesses are paying for part time workers on GoGet.
What is Salaried Pay?
A salaried employee receives a certain amount based on the annual salary or cost-to-company (CTC) broken down into monthly payments.
In Malaysia, employees’ pay is generally based on a 48-hour workweek. However, they may work more than 48 hours and earn overtime. Even for working for 48 hours or less, they will still earn the fixed monthly amount.
The total salary of a full-time employee is the gross salary, and the take home after taxes and deductibles is the net salary. Usually it is easier for salaried employees to apply and obtain financial help such as house or car loans as they are deemed to be financially stable to pay back their loans.
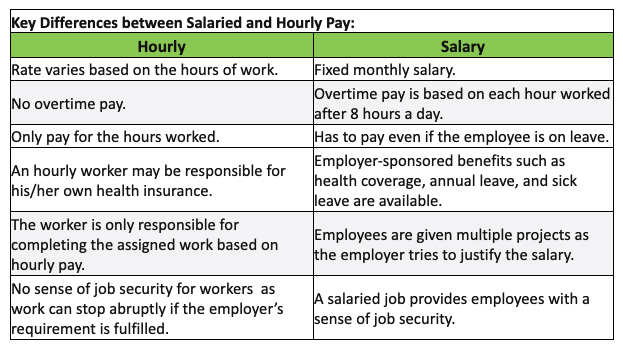
What are the key differences between Hourly and Salaried Pay?
Generally, salaries are for full-time work at a permanent position, and with fixed working hours per week.
Hourly pay in Malaysia is more common in the sectors such as customer service, retail, construction, event management, and hospitality. The work is contract-based where hours may vary from week to week.
The main differences between salaried and hourly workers are not only about pay, they are also linked to benefits and contracts.
Understanding the difference between salaried and hourly work is crucial for you to determine which one is the best for your business and the employees.
How do companies determine Salary vs. Hourly Pay
The decision of companies whether to pay employees salary or hourly depends on whether they are exempt or non-exempt from overtime pay and depends on the job requirement.
It means all the decisions regarding which positions should be salaried or hourly, are based on the complete understanding of the job responsibilities of each position. This is how startups pay employees.
Regardless of whether salaried or hourly, the benefits of paying your employees well are many and you should try to make the most of it.
Here is how companies determine salary vs. hourly pay:
Outline the positions according to professional categories based on resources available.
Write job descriptions for each position for which a company needs to decide to pay salary or hourly basis, including the essential functions.
Review the Malaysian Labour Law for classifications of exempt and non-exempt workers.
Go through overtime pay rules and criteria for executive, administrative, and professional exemptions.
Based on the above steps, including the minimum wage and hourly rate by law, companies decide to hire on a salary or hourly basis.
Share this article
